The Effects of Smoking on Teeth: Understanding the Damage to Oral Health
Smoking is a well-known health hazard, and its effects extend far beyond the lungs. One of the most noticeable and damaging areas affected by smoking is the mouth, particularly the teeth. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can have serious consequences on oral health, leading to a variety of issues such as stained teeth, gum disease, and even tooth loss. In this article, we will explore the various effects of smoking on teeth and offer insights into how these problems can be prevented or mitigated.
1. Stained Teeth and Discoloration
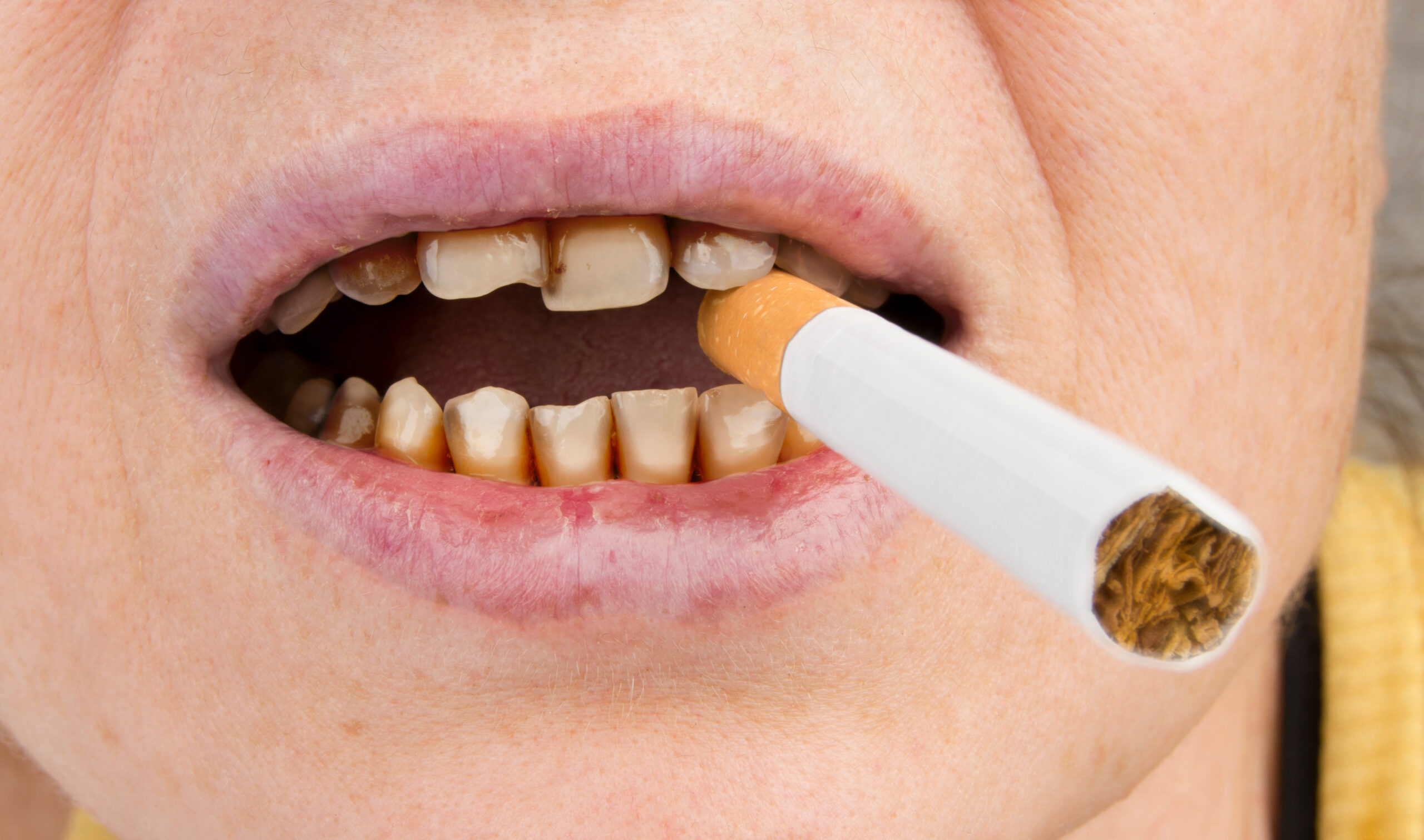
One of the most immediate and visible effects of smoking on teeth is staining and discoloration. The nicotine and tar found in cigarettes are the primary culprits behind this issue. These substances can quickly attach to the enamel of your teeth, causing a yellow or brownish discoloration that can be difficult to remove, even with regular brushing.
Smoking leads to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which can further contribute to a dull, yellow appearance. Over time, these stains can become more stubborn and may require professional cleaning to remove. This discoloration not only affects the appearance of your smile but also impacts your overall confidence.
2. Increased Risk of Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is another significant consequence of smoking on oral health. Smokers are more likely to develop gum disease due to the negative effects that smoking has on gum tissue. The chemicals in cigarettes reduce blood flow to the gums, impairing the body’s ability to fight off infections and heal damaged tissue.
As a result, smokers are at a much higher risk of developing gingivitis (the early stage of gum disease) and periodontitis (advanced gum disease). Symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, as well as bad breath. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to the loss of teeth.
3. Bad Breath (Halitosis)
One of the most common and unpleasant effects of smoking on teeth is bad breath, also known as halitosis. The chemicals in tobacco, along with the dry mouth caused by smoking, can lead to persistent bad breath. In addition, smokers often develop a build-up of plaque and tartar on their teeth, which can also contribute to bad breath.
The tar and nicotine in cigarettes are absorbed by the oral tissues, and their lingering odor can create an unpleasant smell that’s difficult to mask with breath fresheners. Smokers who do not maintain proper oral hygiene are particularly prone to halitosis, making it an embarrassing consequence of smoking.
4. Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common issue among smokers. The harmful chemicals in cigarettes can weaken the enamel of your teeth, making them more vulnerable to hot, cold, or acidic foods and drinks. This can lead to sharp pain or discomfort when consuming certain substances.
As smoking exacerbates the breakdown of enamel, the underlying dentin becomes exposed, leading to an increased sensitivity to temperature changes. Over time, this can make it difficult to enjoy certain foods or beverages without experiencing discomfort.
5. Increased Risk of Tooth Loss
Smoking is a major risk factor for tooth loss. The effects of smoking on gum health and the overall weakening of teeth make smokers more susceptible to tooth decay and eventual tooth loss. Gum disease, which is more prevalent among smokers, is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults.
When gum disease progresses to a severe stage, it can cause the gums to recede, weakening the teeth and leading to the destruction of the bone that supports them. This damage can eventually cause teeth to loosen and fall out. If you are a smoker, the risk of tooth loss is significantly higher compared to non-smokers.
6. Slower Healing Process After Dental Procedures
Another effect of smoking on teeth is the delayed healing process after dental procedures. Whether it’s a simple cleaning, a tooth extraction, or more complex procedures like implants or gum surgery, smoking can slow down the healing process. This is because smoking reduces blood flow to the gums, which impairs the body’s ability to heal effectively.
For individuals who have recently undergone dental procedures, smoking can increase the risk of complications, such as infection or poor tissue regeneration. This can prolong recovery time and potentially affect the success of the procedure.
7. Increased Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Smoking accelerates the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, while tartar is hardened plaque that can only be removed by a dental professional. Smokers often experience a higher amount of plaque buildup due to the chemicals in tobacco, which encourages bacterial growth.
This excess plaque and tartar can lead to cavities, gum disease, and other oral health problems. Regular brushing and flossing are essential to help reduce plaque buildup, but smokers may find it more challenging to keep their teeth clean due to the effects of smoking.
8. How to Mitigate the Effects of Smoking on Teeth
While the effects of smoking on teeth can be severe, there are steps smokers can take to reduce damage and maintain better oral health. Here are some tips:
- Quit Smoking: The most effective way to protect your teeth and gums is to quit smoking. This will reduce your risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Smokers should visit their dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. This will help remove plaque and tartar buildup and allow the dentist to identify any potential oral health issues early.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to reduce plaque buildup. Using a mouthwash designed for smokers can also help combat bad breath.
- Teeth Whitening: If you smoke and have stained teeth, consider teeth whitening treatments. A dentist can help restore the whiteness of your teeth and improve your smile.
Conclusion
The effects of smoking on teeth are far-reaching and can lead to significant oral health problems, including stained teeth, gum disease, bad breath, and tooth loss. By quitting smoking and adopting a strong oral hygiene routine, you can reduce the risks associated with smoking and improve your overall oral health. If you are a smoker, it is crucial to take steps to protect your teeth and gums, and seek professional dental care to address any issues promptly.